High-Tech Opportunities for Education and Training

Immersive technologies are rapidly changing the way people work and play. New digital devices such as iPhone X have been released to facilitate technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) on handheld devices and headsets. As these technologies gain popularity, more immersive experiences are expected to emerge. The education sector has already recognized the enormous potential of immersive technologies in teaching.
Research has shown that scenario-based VR training provides learners richer, lowercost content than text, pictures, audio, and video materials in face-to-face training. It also influences learners’ behavior more effectively than training in traditional classrooms or other digital forms. The biggest highlight of VR training is that it empowers learners with an immersive experience free from potential safety risks in real-life scenarios.
Unlike VR technology that creates immersive environments through computers, AR technology overlays information such as computer-generated images onto the user’s view of the real world. AR training solutions need no human actions to provide context and relevant information at action points during instructional training. For example, warehouse workers and equipment maintenance personnel can be provided the necessary information to improve work efficiency, streamline communication, interact with customers, and optimize maintenance.
As hardware becomes more affordable and creative tools mature, immersive technologies combining VR and AR have generated one of the most valuable methods of online learning. In the vocational training market, companies are showing a stronger interest and willingness than individual learners to explore and adopt immersive technologies and offer employees a highly simulated learning experience with ample opportunities for practice.
In many cases, virtual activities enabled by immersive technologies can replace costly real-life learning activities that require learners to gather in a certain spot with necessary equipment, technology, and safety experts. Such training usually demands on-site courses in specially designed venues. For example, an insurance adjuster learns to inspect vehicle damage in a full-size model room, and an engineer learns to handle emergencies such as a transmission accident or power failure using a generator that has been retired or dedicated to training.
Digital training based on immersive technologies can help learners grasp a variety of skills that in the past could only be honed in a real-life working environment. The ability of AR and VR technologies to reduce training costs by stimulating realistic scenarios and removing the need for physical equipment or massive personnel movement has made it a strategic focus for many companies. This is especially true in the post-COVID world in which business travel and face-toface training have become more challenging.
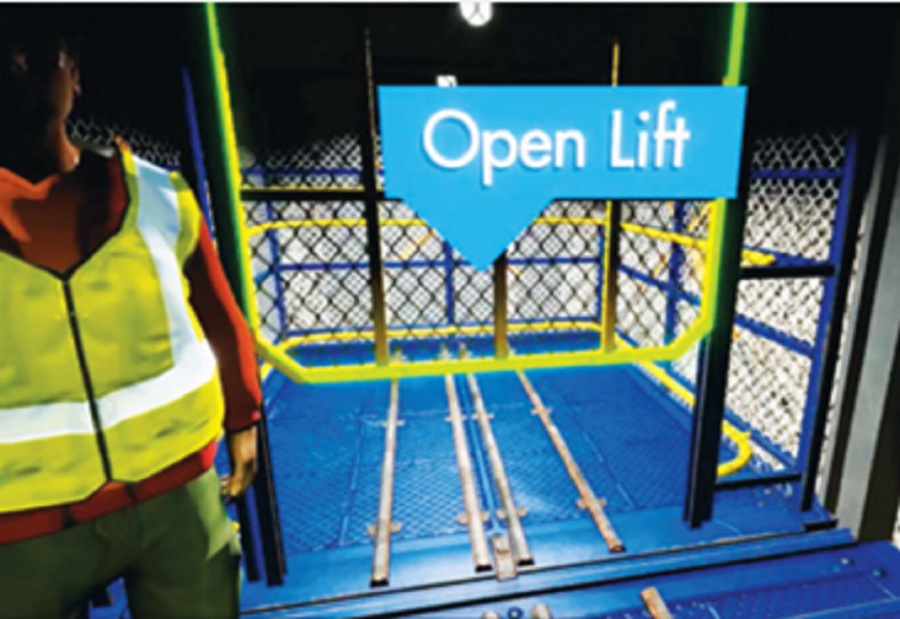
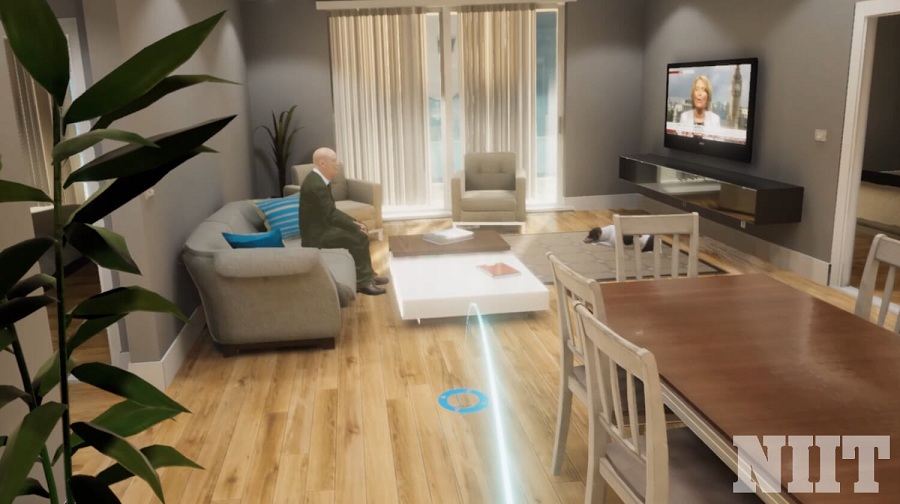
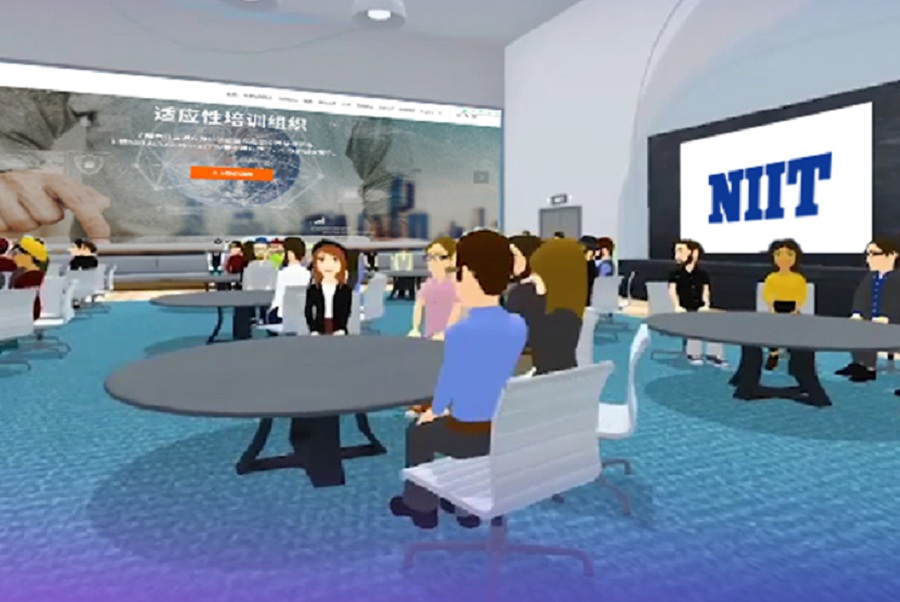


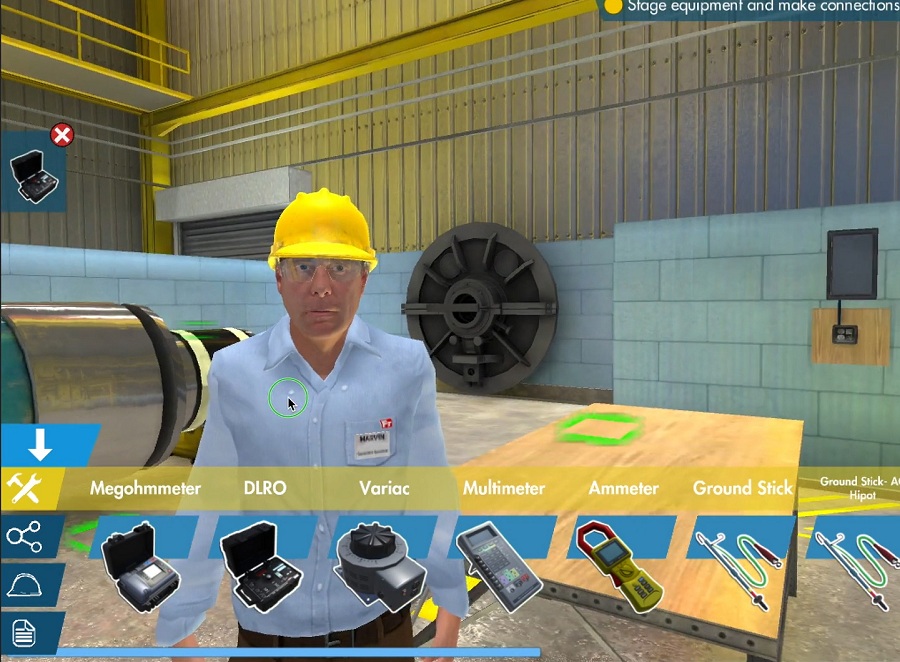

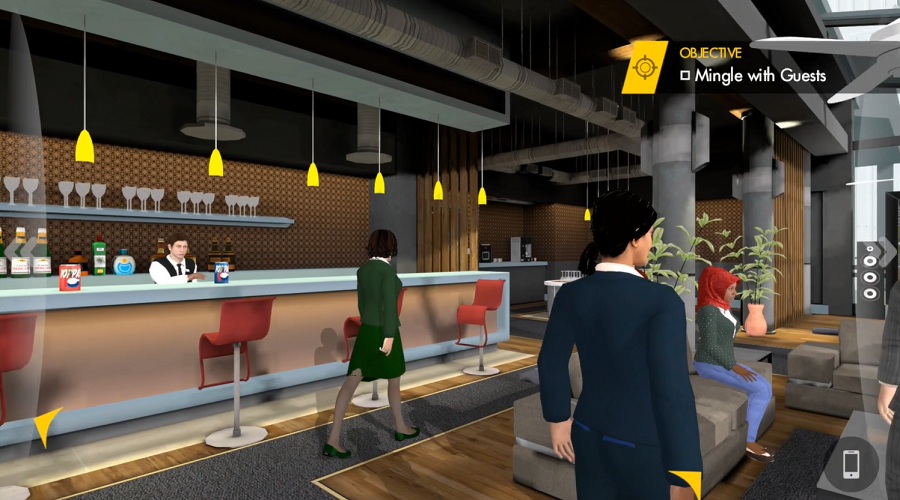
As one of the world’s largest information technology training and talent development companies, the National Institute of Information Technology (NIIT) in India has developed learning and teaching products in collaboration with many partners and gained extensive experience applying gamification, VR, and AR technologies in training. Here are a few examples:
Gamification has been applied in a leadership training program for corporate executives. The program was designed for a global energy and petrochemical group hoping to retool its existing training on business ethics and legal compliance. It was designed for senior executives of subsidiary companies and focused on complex real-life and everyday issues related to business ethics and legal compliance. In response to these needs, NIIT created a real-time 3D game to provide experiential learning content. Following a learning-by-doing approach, the training course aims to motivate executives to break through the slow pace of traditional courses and think quickly to foster business development.
A training program was created through a VR game to simulate safety drills in underground mining scenarios. The game adopted a first-person perspective to be deployed through HTC Vive headsets. It empowers learners to navigate complex mines to mark and fix safety problems as they move forward in the game. If learners fail to solve emerging problems quickly, they will “experience” the consequences of serious disasters such as personnel injuries, mine collapses, and massive hypoxia and asphyxia. In addition to making the game more engaging, these experiences have an important role in teaching: By triggering emotional responses in learners, the experiences result in more accurate retention of memories associated with the emotional reactions, which in turn ensure that better learning results transfer to work in the real world. This training solution is usually deployed at the client company’s safety production drill laboratory outside its mining site.
A VR training game was created for home inspections in the real estate industry. Simulating real-life scenarios, the game also adopted a first-person perspective to be deployed through HTC Vive devices. The game helps new employees in the real estate industry learn how to inspect homes, identify possible defects that might affect the price, determine the cost impact of each defect, and observe the long-term impact of their decisions on negotiations with clients. Contrasting previous training programs that have had little success helping learners understand the consequence of a poor home inspection, this training solution has been more efficient by providing more timely and effective feedback.
A training application for electrical testing was designed for a manufacturing company. The mobile-based application helps electrical engineers in a global manufacturing company perform several basic tests in electrical operations and obtain relevant industry certifications.
A Python data analysis course has been developed combining a traditional online classroom and a metaverse learning community. NIIT China conducts many digital talent training sessions every year. The data analysis course launched by its subsidiary StackRoute in 2022 has adopted the form of a metaverse learning community in which students can create their own digital images and interact with the instructor and classmates in the metaverse for a better immersive learning experience.
According to research published by PricewaterhouseCoopers, compared to classroom learners, VR-trained learners were 3.75 times more emotionally connected to the content, completed training an average of four times faster than classroom training, and were up to 275 percent more confident to act on what they learned after training. A strong consensus has emerged that training solutions based on VR, AR, and other metaverse-related technologies such as gamified teaching programs have the potential to exponentially increase the opportunities for talent development in various industries.
The author is head of business development of corporate learning at NIIT China.